
UMBRA ECLIPSE DEFINITION FULL
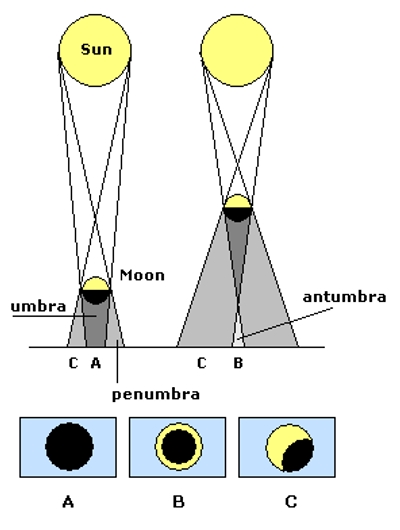
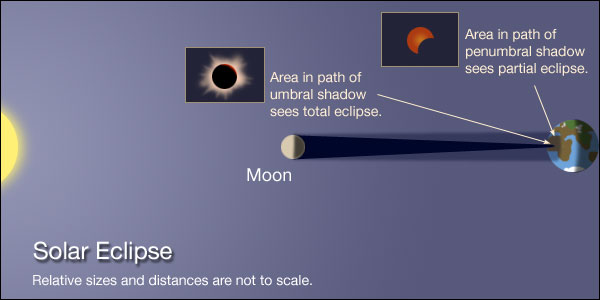
Now you might be wondering "If the Moon orbits Earth every 29.5 days and lunar eclipses only occur at Full Moon, then why don't we have an eclipse once a month during Full Moon?". These events are quite striking due to the Moon's vibrant red color during the total phase (totality).The entire Moon passes through Earth's umbral shadow.These events are easy to see, even with the unaided eye.A portion of the Moon passes through Earth's umbral shadow.These events are of only academic interest because they are subtle and hard to observe.The Moon passes through Earth's penumbral shadow.In contrast, the inner or umbral shadow is a region where the Earth blocks all direct sunlight from reaching the Moon.Īstronomers recognize three basic types of lunar eclipses: The outer or penumbral shadow is a zone where the Earth blocks part but not all of the Sun's rays from reaching the Moon. That shadow is actually composed of two cone-shaped components, one nested inside the other. Geometry of the Sun, Earth and Moon During an Eclipse of the Moon Earth's two shadows are the penumbra and the umbra.Īn eclipse of the Moon (or lunar eclipse) can only occur at Full Moon, and only if the Moon passes through some portion of Earth's shadow. It happens because the Moon is directly opposite the Sun in the sky when the Moon is Full.įull Moon also has special significance with regard to eclipses.

None of the Moon's other phases have this unique characteristic. When the Moon is Full, it rises at sunset and is visible all night long.Īt the end of the night, the Full Moon sets just as the Sun rises. The Full Moon is popularly known as the phase of love and romance. In comparison, the Full Moon phase occurs mid-way through the lunar month. The New Moon phase is uniquely recognized as the beginning of each calendar month just as it is the beginning on the Moon's monthly cycle. The Hebrew, Muslim and Chinese calendars are all lunar calendars. In fact, some calendars are synchronized to the phases of the Moon. Many early civilizations used the Moon's monthly cycle to measure the passage of time. The rest of the phases are familiar to all of us as the Moon cycles through them month after month.ĭid you realize that the word month is derived from the Moon's 29.5 day period? The phase known as New Moon can not actually be seen because the illuminated side of the Moon is then pointed away from Earth. Waning Gibbous > Last Quarter > Old Crescent > New Moon (again)
UMBRA ECLIPSE DEFINITION SERIES
The Moon orbits Earth about once every 29 and a half days.Īs it circles our planet, the changing position of the Moon with respect to the SunĬauses our natural satellite to cycle through a series of phases:

It has no light of its own but shines by sunlight reflected from its surface. The Moon is a cold, rocky body about 2,160 miles (3,476 km) in diameter. You'll learn the answers to these questions and more in MrEclipse's primer on lunar eclipses. How often do eclipses happen and when is the next eclipse of the Moon?
Draw in the incident rays corresponding to these angles and label them A, B, C.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
